Blockchain Explained: Everything You should Know about Blockchain Technology
Blockchain is a distributed database technology that allows multiple parties to maintain a shared and tamper-proof ledger of transactions. It was originally developed for the cryptocurrency Bitcoin, but it has since been applied to many other areas.
A blockchain consists of a chain of blocks, where each block contains a set of transactions. The blocks are linked together using cryptography, forming a continuous and unalterable chain. Each block also contains a unique cryptographic signature, called a hash, which is generated based on the data in the block. This makes it impossible to modify a block without changing its hash, which would invalidate the entire chain.
One of the key features of blockchain is its decentralized nature. Instead of having a central authority or intermediary, each participant in the network has a copy of the entire blockchain, and all transactions are validated by consensus among the participants. This makes the system more secure, since there is no single point of failure, and it also increases transparency, since all participants can see the same information.
Blockchain has a wide range of potential applications, including financial services, supply chain management, healthcare, and voting systems. It is often touted as a more secure and efficient alternative to traditional databases, but it is not without its limitations and challenges, including scalability, interoperability, and regulatory issues.
Blockchain in simple terms!
Imagine you have a notebook where you write down all your transactions, such as buying groceries or paying rent. Now, imagine that everyone you know also has a similar notebook, and they write down their transactions in their own notebooks too.
In a blockchain system, these notebooks are replaced by digital ledgers, and each transaction is recorded as a block in the ledger. But unlike a physical notebook, these digital ledgers are stored on many computers all over the world, not just in one place.
Each block in the ledger has a unique "digital signature" that makes it impossible to change or delete once it's been added to the chain. This means that once a transaction is recorded in the ledger, it can't be altered, making the system very secure.
So, why would we want to use a blockchain instead of just a regular database? Well, one advantage is that it allows multiple parties to trust and verify transactions without relying on a central authority, such as a bank. For example, if you wanted to send money to a friend in another country, you could use a blockchain system to do so without needing to go through a bank or other financial institution.
Another advantage is that blockchain can help prevent fraud and ensure transparency in industries such as supply chain management. For instance, a company could use a blockchain system to track the journey of a product from the manufacturer to the store shelves, allowing consumers to verify that the product is genuine and hasn't been tampered with.
Overall, blockchain is a way of creating secure, decentralized digital ledgers that can be used for a variety of purposes. While it's a complex technology, the basic idea is that it allows us to create trust and transparency in a way that wasn't possible before.
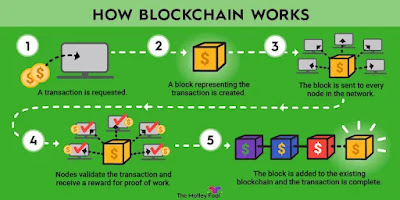
How Blockchain Technology Work?
At a high level, blockchain technology works by creating a digital ledger of transactions that is maintained across a network of computers. This ledger is constantly updated and verified by the network, and it is secured by cryptography to ensure the integrity of the data.
Here is a more detailed explanation of how blockchain technology works:
Transactions: The blockchain ledger is made up of a series of transactions, which can be anything from cryptocurrency transactions to the exchange of digital assets. Each transaction is verified by the network before it is added to the ledger.
Blocks: Transactions are grouped together into blocks, which are added to the blockchain in a sequential order. Each block contains a unique code called a "hash" that identifies it, as well as a reference to the previous block in the chain.
Distributed network: The blockchain ledger is maintained by a distributed network of computers, also known as nodes, that work together to validate transactions and add new blocks to the chain. Each node has a copy of the entire blockchain ledger, so if one node goes offline, the rest of the network can continue to function.
Consensus: To ensure the integrity of the blockchain ledger, the network must reach a consensus on the order and validity of transactions. This is typically achieved through a consensus algorithm, which is a set of rules that govern how the network reaches agreement on which transactions should be added to the blockchain.
Cryptography: Blockchain technology uses cryptography to ensure the security and privacy of the data stored on the blockchain. Each transaction is encrypted using a public-key cryptography system, which means that only the owner of the private key can access the data.
Overall, blockchain technology is a decentralized, secure, and transparent way of recording and verifying transactions that has the potential to transform a wide range of industries.
The future of blockchain is quite promising!
The future of blockchain is quite promising, as it has the potential to revolutionize many industries and areas of our lives. Here are a few possible ways that blockchain could impact the future:
Financial Services: Blockchain technology can enable faster, cheaper and more secure financial transactions without intermediaries such as banks, and provide access to financial services for the unbanked population. Decentralized finance (DeFi) is a growing industry that uses blockchain to offer a range of financial services including lending, borrowing, and trading.
Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can help increase transparency and accountability in supply chains, by tracking the movement of goods and verifying their authenticity. This can help reduce fraud, improve product quality and safety, and enable consumers to make more informed purchasing decisions.
Digital Identity: Blockchain can be used to create secure digital identities, giving people more control over their personal data and enabling them to prove their identity without relying on third parties. This could have applications in areas such as voting systems, healthcare, and social media.
Internet of Things (IoT): The use of blockchain technology can enable secure, decentralized and transparent communication between devices in IoT networks, ensuring that data is not tampered with and is transmitted only to authorized parties.
Energy and Environment: Blockchain can be used to create decentralized energy grids and enable peer-to-peer energy trading, making renewable energy more accessible and reducing dependence on centralized energy providers. It can also help to monitor and reduce carbon emissions and improve environmental sustainability.
Bitcoin (BTC): The first and most well-known blockchain platform, Bitcoin is a decentralized, peer-to-peer digital currency that allows for secure, transparent and fast transactions without the need for intermediaries. Its native token is BTC.
Ethereum (ETH): Ethereum is a blockchain platform that allows developers to build decentralized applications (dApps) using smart contracts, which are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement between buyer and seller being directly written into lines of code. Its native token is ETH.
Binance Smart Chain (BSC): Binance Smart Chain is a blockchain platform developed by the cryptocurrency exchange Binance, which is designed to provide faster and cheaper transactions than the Ethereum network. Its native token is BNB.
Cardano (ADA): Cardano is a blockchain platform that uses a proof-of-stake consensus algorithm to secure its network and enable faster and cheaper transactions than other blockchain platforms. Its native token is ADA.
Polkadot (DOT): Polkadot is a blockchain platform that allows different blockchains to connect and work together, making it easier for developers to build and deploy decentralized applications. Its native token is DOT.
Solana (SOL): Solana is a high-performance blockchain platform that can handle a high volume of transactions with low fees. Its native token is SOL.
Overall, the future of blockchain looks bright, as the technology continues to evolve and be applied in new and innovative ways. While there are still challenges to be overcome, such as scalability, interoperability, and regulatory issues, the potential benefits of blockchain are vast, and it's likely to play an increasingly important role in our lives in the years to come.
Leading blockchain platforms and their associated tokens:
These are just a few examples of the many blockchain platforms and tokens that are currently available. Each platform has its own unique features and use cases, and new platforms and tokens are being developed all the time.



No comments:
Post a Comment